Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol that enables network communications to reach a specific device on the network. ARP translates Internet Protocol (IP) addresses to a Media Access Control (MAC) address, and vice versa. Most commonly, devices use ARP to contact the router or gateway that enables them to connect to the Internet.
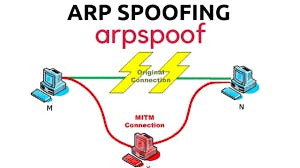
An ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a Man in the Middle (MitM) attack that allows attackers to intercept communication between network devices. The attack works as follows:
What is Arp Spoofing?
An ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a Man in the Middle (MitM) attack that allows attackers to intercept communication between network devices. The attack works as follows:
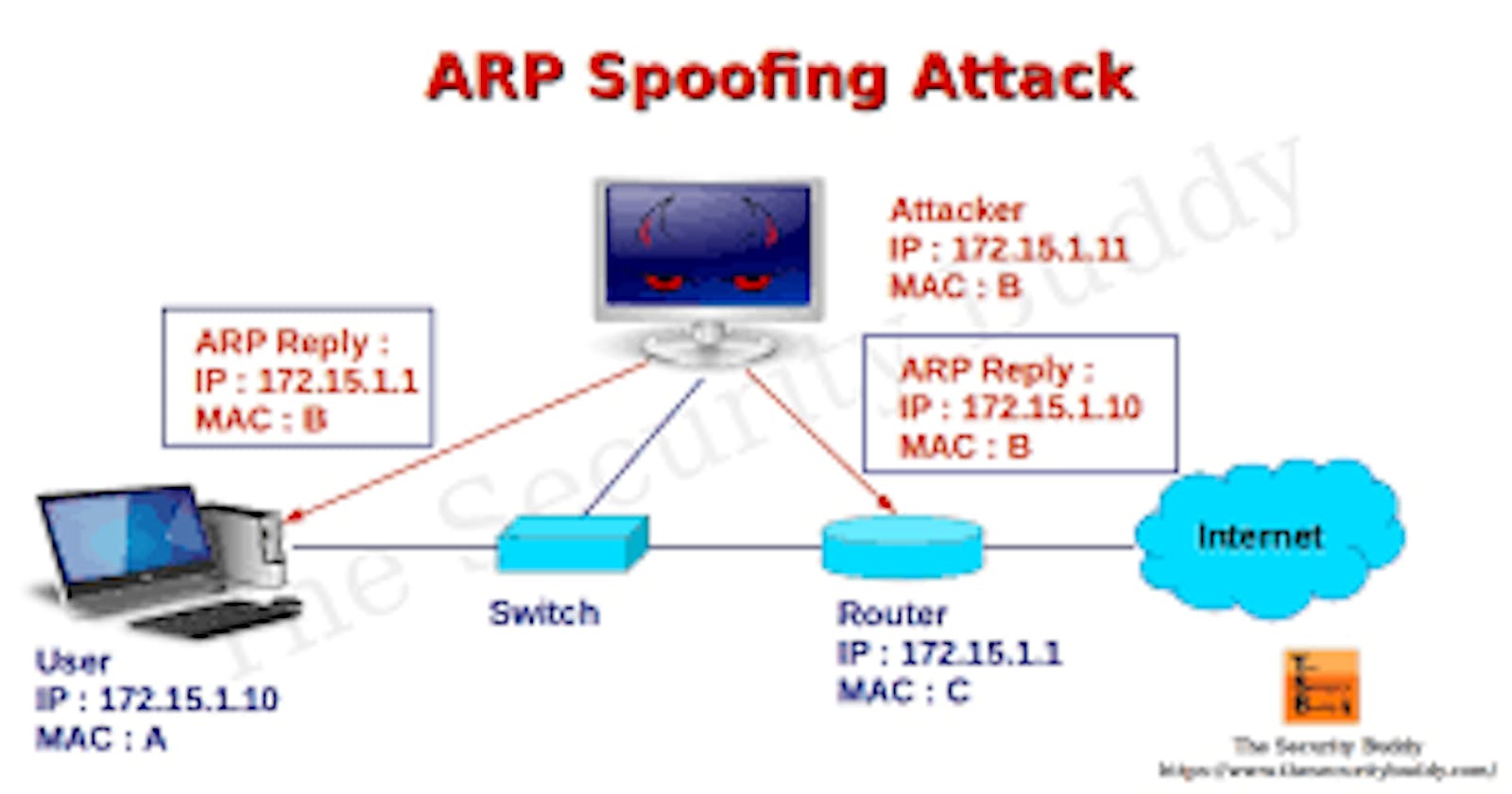
1.The attacker must have access to the network. They scan the network to determine the IP addresses of at least two devices—let’s say these are a workstation and a router.
2.The attacker uses a spoofing tool, such as Arpspoof or Driftnet, to send out forged ARP responses.
3.The forged responses advertise that the correct MAC address for both IP addresses, belonging to the router and workstation, is the attacker’s MAC address. This fools both router and workstation to connect to the attacker’s machine, instead of to each other.
4.The two devices update their ARP cache entries and from that point onwards, communicate with the attacker instead of directly with each other.
5.The attacker is now secretly in the middle of all communications.